Difference between revisions of "Load-balancing"
(→Resources) |
(→Entities) |
||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
== Entities == | == Entities == | ||
| − | '''Small | + | <p>'''Small request'''<br /> |
| − | '''Standard | + | text |
| − | '''Large | + | </p> |
| − | '''D-DoS'''<br /> | + | <p>'''Standard request'''<br /> |
| + | text | ||
| + | </p> | ||
| + | <p>'''Large request'''<br /> | ||
| + | text | ||
| + | </p> | ||
| + | <p>'''D-DoS'''<br /> | ||
| + | text | ||
| + | </p> | ||
== Resources == | == Resources == | ||
Revision as of 15:53, 17 January 2016
Introduction
Contents
Problem definition
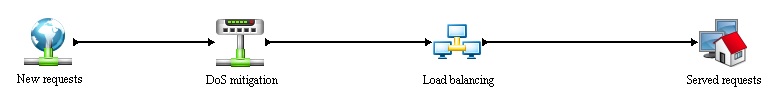
A hosting company with it’s own infrastructure is using so called "load balancing" to distribute the overall load between multiple servers (hardware) and “high-availability” to minimize service down-time.
Load-balancing
short text here
High-avaibility
short text here
Method
SIMPROCESS
Model
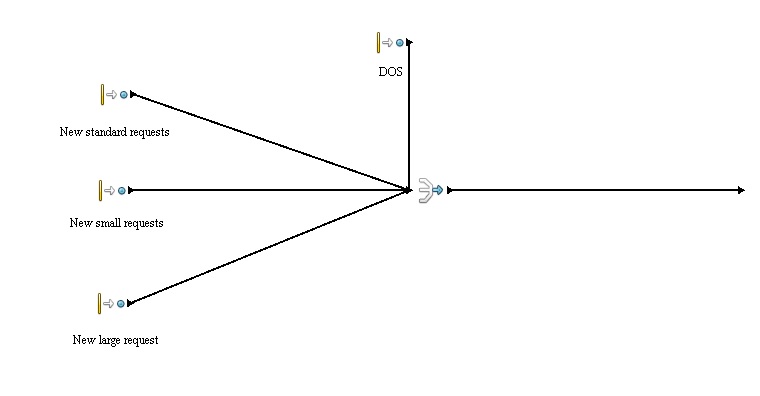
Entities
Small request
text
Standard request
text
Large request
text
D-DoS
text
Resources
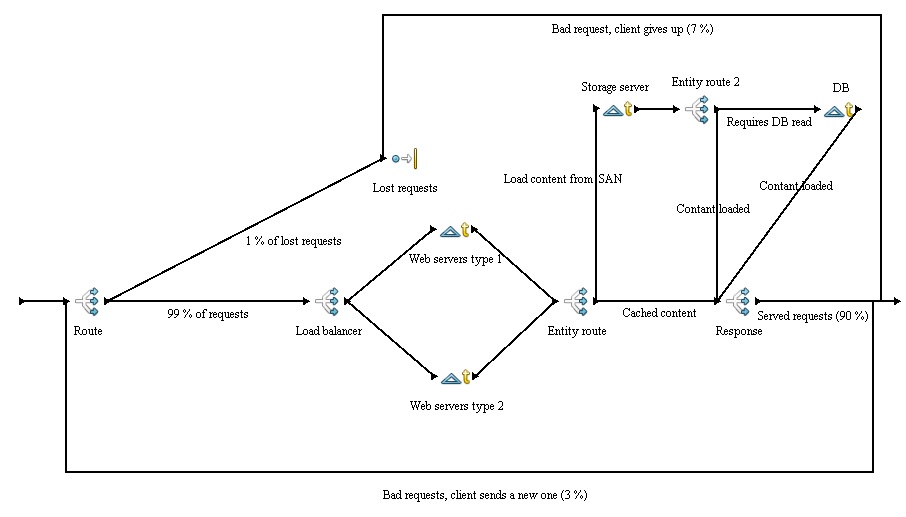
Load-balancer
text
Web server
There are two types of this resource, each with different capabilities:
Type 1
Type 2
Storage server SAN
text
Database server
text
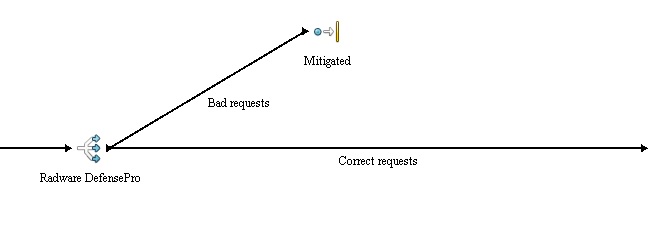
Radware DefensePro
text
Processes
HTTP requests