Load-balancing
- Project name: Load-balancing
- Class: 4IT496 (WS 2015/2016)
- Author: Bc. Patrik Tomášek
- Model type: Discrete-event simulation
- Software used: SimProcess, trial version
Contents
Problem definition
A hosting company with it's own infrastructure is using so called "load balancing" to distribute the overall load between multiple servers (hardware nodes) and “high-availability” to minimize service down-time.
Load-balancing
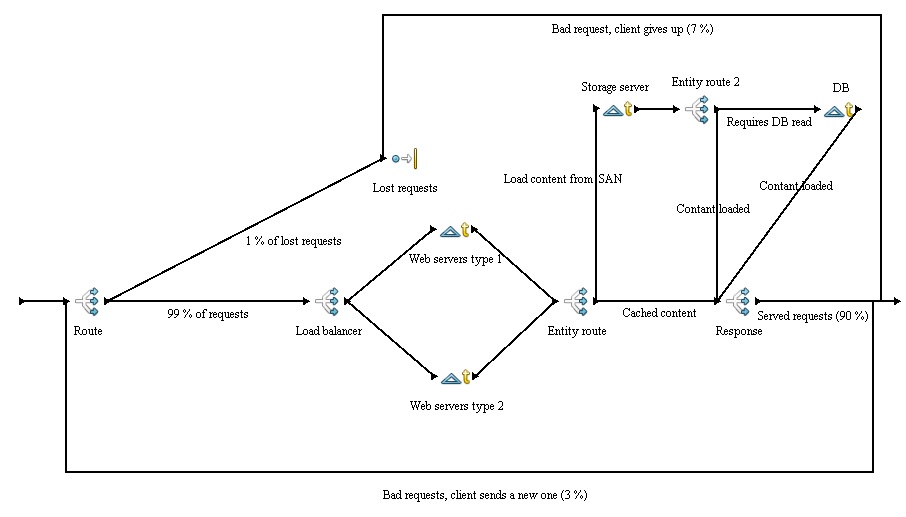
In the case of web hosting service it means dividing the incoming request between multiple devices (called nodes) based on a set of rules (priority, weight, etc). The simulation is based on nginx load balancing.
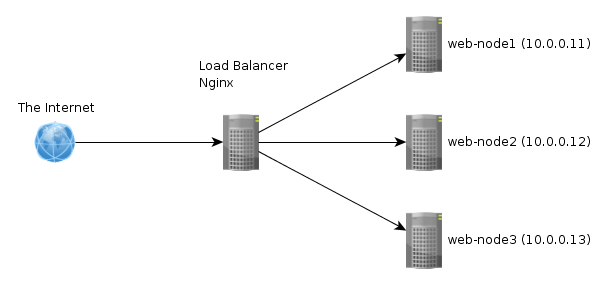
Note: In the picture the load-balacer isn't redundant, therefore HA isn't enabled. The simulation has two load-balances present.
High-avaibility
Ensures that a system or component is operational for desirable time. The solution necessary to provide web hosting consists of many parts, where all of them need to be on-line for the whole to be operational.
To enable HA a provider can use failover and backups. Failover is basically a backup piece of hardware, which ensures that when a component goes off-line another takes it's place. After that it's necessary to load the backup on the component that took over. If there is a SAN (storage area network) implemented than there is no need to load a backup, because failover just uses the same data from one central storage, which is used for all the server nodes. In the simulation a SAN is implemented and failover is taken into consideration.
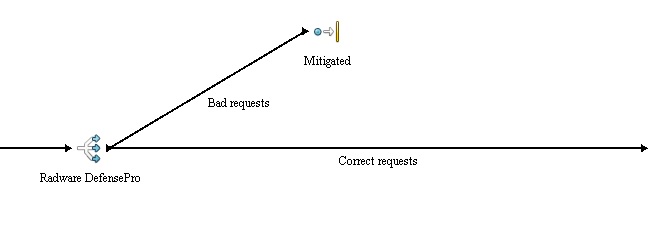
Anti-DoS/DDoS
Denial-of-service (DoS) attack is an incident is witch the targeted service goes down. Distributed denial-of-service means, that more than one system is used to attack a single target. There are more means of possible protection against such attack. Setting up a decent firewall rules might be a good place to start, but it isn't so effective as implementing a device, which can mitigate the attack. A Radware defencePro device is implemented in the simulation.
Method
SIMPROCESS
Model
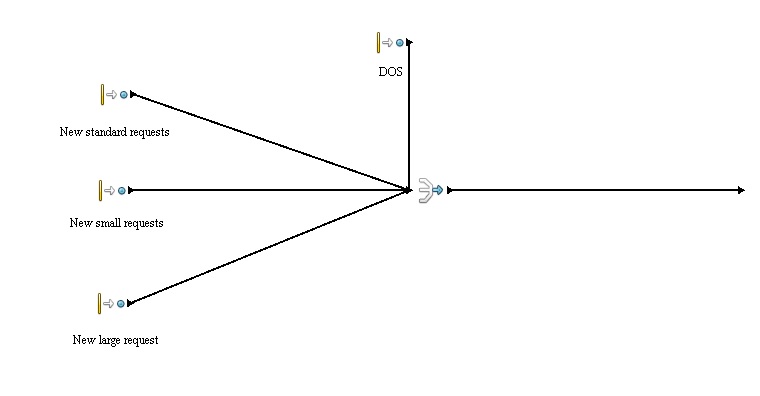
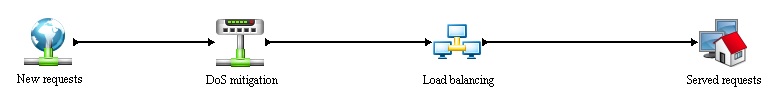
The simulation is divided into 4 main processes:
- New requests - generation of new requests, further information in Entities section.
- DoS mitigation - implementation of anti-dos device.
- Load balancing - main process, witch distributes the generated (incoming) request between resources.
- Served request - simple dispose of the generated requests.
Entities
This is a list of all defined and used entities within the simulation.
Requests
The request data are based on real data from an hosting environment, that hosts multiple Magento e-shops (a rather complex system, which uses a lot of hardware).
The incoming request are categorised because Magento uses caching and indexing. It takes less time to server a cached content than un-cached one. Further more there are multiple schedules used to generate the requests. If new data have been added to the e-shop, that they need to be cached first, witch means more large requests.
- Small request
Request of a cached content.
- Standard request
Request of a content on storage server, no need to accesses database.
- Large request
Request of a content on storage server and database.
D-DoS
A large number of requests aiming to cripple the system.
Resources
Load-balancer
An important component described earlier on this page.
These devices are quite expensive. In case of lease, the price can be 300 USD monthly for a sufficient component for this simulation requirements.
Web server
There are two types of this resource, each with different capabilities:
Type 1
Type 2
Storage server SAN
text
Database server
text
Radware DefensePro
text
Processes
HTTP requests